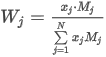Appendix - Mathematical Formulas
Match Factor
The Match Factor is calculated using the normalized spectral data on the basis of the Match Criteria selected in the Chromatogram - Measurement Conditions - PDA Method tab. In case the measured and library spectra do not have the same wavelength range, only their overlap is evaluated (selecting the higher minimum wavelength and the lower maximum wavelength from two spectra). In case the number of spectral points in this interval differs (the step size is different), the library spectrum is interpolated to match the wavelengths of the points in the measured spectrum.
Normalization
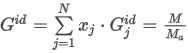
where ai,norm is the normalized spectral point value (absorbance) at wavelength i, ai is the spectral point value at wavelength i, amax is the maximum point value in the spectrum and amin is the minimum point value in the spectrum.
Match Criteria: Least Square
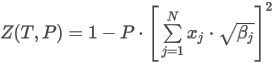
where the sum is taken over all N points of the spectrum and:
ai is the normalized point value of the measured spectrum in the apex
bi is the normalized point value of the library spectrum
N is the number of spectral points
Match Criteria: Weighted Least Square
where the sum is taken over all N points of the spectrum and:
ai is the normalized point value of the measured spectrum in the apex
bi is the normalized point value of the library spectrum
N is the number of spectral points
The points where ai+bi=0 are omitted from the calculation (number of spectral points N is not adjusted).
Match Criteria: Correlation
The correlation match factor is calculated as the Pearson Correlation Coefficient (R) is rescaled to interval [0,1000]:
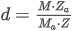
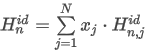
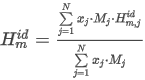
where the sum is taken over all N points of the spectrum and:
ai is the normalized point value of the measured spectrum in the apex
bi is the normalized point value of the library spectrum
N is the number of spectral points.
Peak Purity
Depending on the calculation setting selected in the Chromatogram - Measurement Conditions - PDA Method tab, Used Points section, the following data points are considered in the Peak Purity calculation:
- All - the spectrum of each data point from a selected interval is compared to the spectrum of the apex; the obtained values are averaged. The interval is defined by the set Absorbance Threshold. The interval start and end are identified as the points where the height of the signal over baseline is higher (lower) than the set Absorbance Threshold, which is defined as percent (%) of the detected peak height. When set to 0%, the entire peak is covered.
- Five - spectra of five significant peak points are compared to the apex spectrum; the obtained values are averaged. The selected five points are the peak purity start, peak purity inflex, peak apex, the second peak purity inflex, and peak purity end. The peak purity start spectrum is taken as the point spectrum in one-third of the distance between the inverval start and the peak apex. The peak purity inflex spectrum is taken as the spectrum of the point in two-thirds of the distance between the interval start and the peak apex. For the peak purity end and the other peak purity inflex, the situation is analogous. The set Absorbance Threshold is taken into account for identification of the interval start and end.
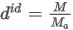
The data are not normalized for the calculations. Peak Purity is calculated by averaging the Pearson Correlation Coefficients (R) of each considered data point rescaled to interval [0,1000]:
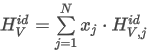
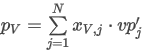
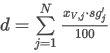
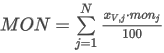
where the sum in fraction coefficient xpoint is taken over all N points of the spectrum and:
ai is the spectral point value at wavelength i of each point according to the selected Used Points option
bi is the spectral point value at wavelength i at RT max (apex)
N is the number of spectral points.
Background Correction
Using the Background Correction is optional for calculation of the Match Factor (Library Search Options) and Peak Purity (Peak Purity Options). The calculation is based on interpolating the baseline for individual spectral points (absorbances) between the peak start and peak end points. For each data point considered in the calculation (i.e., apex for Match Factor, all points or five significant points for Peak Purity), the spectral point values are corrected by the background correction factor (BCF), which is calculated as:
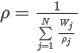
where:
BCFi,point is the background correction factor of the spectral point value at wavelength i of the data point according to the calculation type as mentioned above (e.g., apex...)
ci is the spectral point value at wavelength i of the peak start
di is the spectral point value at wavelength i of the peak end
nstart, nend, npoint is data point number of the peak start, peak end, or the data point according to the calculation type as mentioned above
The background correction factor is then subtracted from each spectral point value at wavelength i of the data point considered in the subsequent calculation: